Ultra wideband (UWB or Ultra-wideband) is a wireless technology that uses radio wave pulses to send data over short distances. It has a super wide bandwidth, which means it can transfer data really fast and track locations with great accuracy.
The fundamentals of UWB technology, possible applications, and issues that still need to be resolved before it can be extensively used will all be covered in this article. UWB is a promising new technology with a wide range of potential applications, including:
- Proximity sensing and tracking: Ultra-wideband may be used to accurately track the movement of persons or things. The management of crowds, asset monitoring, and gesture detection are just a few areas in which it performs well.
- Precise positioning: UWB is great for finding device locations quite accurately. It can be very useful for GPS navigation, augmented reality, and self-driving cars like Robotaxi.
- High-speed data transfer: UWB is super fast at transferring data, even if it’s just a short distance. It’s ideal for stuff like sharing files, streaming media, and gaming.
- Security: Secure wireless networks that are robust to interception and intercepting may be built using UWB. This can be very useful for financial transactions and military communications.
How Does UWB Work?
UWB works by transmitting short, high-power radio pulses. Because each pulse has a significantly smaller width than the radio pulses’ wavelength, UWB has a very broad bandwidth. The distance between the two devices is determined utilizing how much time it takes for the pulses to get from the transmitter to the receiver.
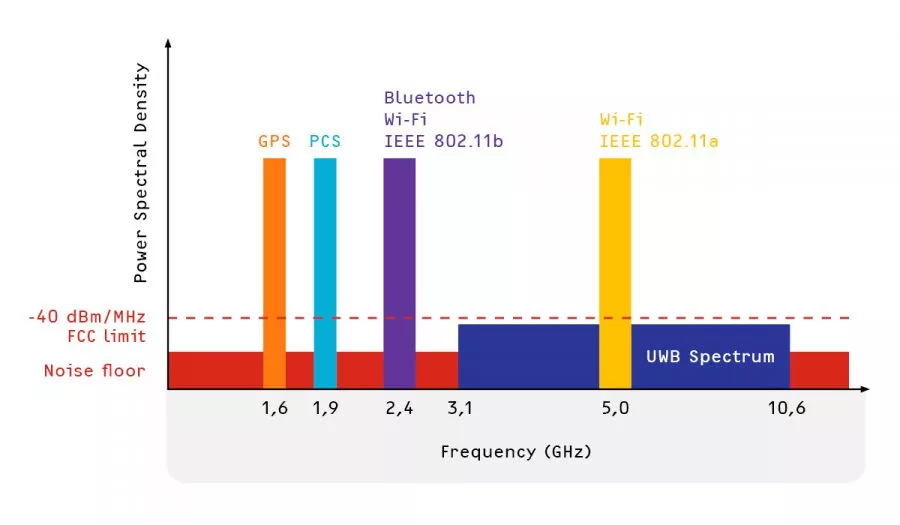
How is UWB Different From WiFi and Bluetooth?
- Frequency Range: Compared to Bluetooth and WiFi, UWB uses a much larger frequency spectrum. While UWB uses a wide variety of frequencies from 3.1 GHz to 10.6 GHz, Bluetooth and WiFi both operate in the 2.4 GHz frequency spectrum. UWB can carry data at quicker rates and with higher accuracy due to its wider frequency spectrum.
- Data Rate: Comparing UWB to Bluetooth and WiFi, the data rates are considerably larger. While WiFi may deliver data speeds ranging from Mbps to Gbps, Bluetooth normally supports data rates up to a few Mbps. UWB, on the other hand, may reach data speeds of up to several Gbps, making it appropriate for applications that need incredibly quick and dependable data transfer.
- Power Consumption: UWB technology is more energy-efficient than Bluetooth and WiFi since it is made to function at low power levels. With the aid of this technology, devices that use batteries may now operate for extended periods of time between charges and energy-efficient wireless sensor networks can be created.
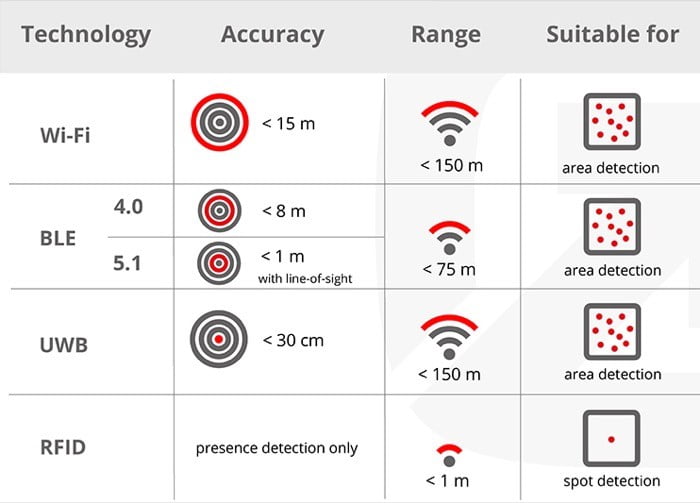
- Precision and Range: The high level of accuracy of UWB’s tracking capabilities is higher than those of Bluetooth and WiFi. UWB can measure distances between objects with centimeter-level accuracy, allowing applications like indoor positioning systems and real-time location tracking.
- Interference and Coexistence: Because UWB technology runs on a larger frequency range and uses a different modulation method, there is less chance that it would interact with other wireless systems. This prevents severe performance reduction when UWB devices coexist alongside Bluetooth and WiFi devices.
Ultra Wideband Technology and Its Applications
Here are some Applications of UWB:
UWB is a tracking technology that is very accurate and can locate objects within a few centimeters. Other tracking methods like Bluetooth and GPS are only accurate within a few meters. UWB is used in devices like Apple AirTag and Samsung Galaxy SmartTag Plus.
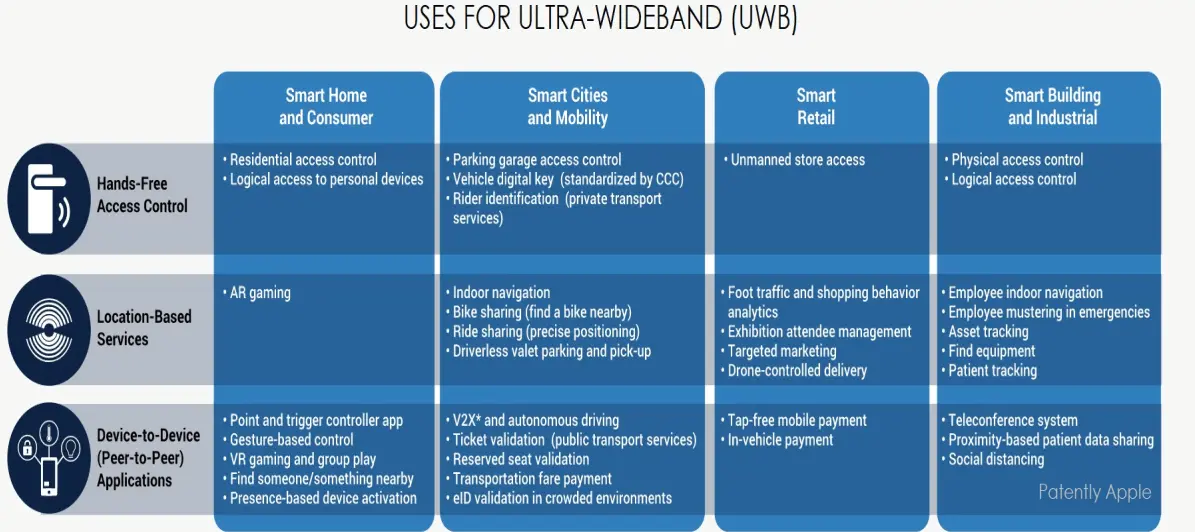
In the future, UWB could be used as a secure digital key for cars, allowing for real-time location tracking of the key fob.
UWB can also be embedded in smartphones and smartwatches for convenience. Samsung is working on a Digital Key platform that would allow users to unlock their front door with a UWB-enabled device or wearable.
Here is a list of smartphones and wearables that support UWB technology: Apple iPhone 11, 12, 13, and 14 series, Google Pixel Fold, Pixel 6 Pro, 7 Pro, Samsung Galaxy S21 Plus/Ultra, S22 Plus/Ultra, S23 Plus/Ultra, Note 20 Ultra, and Apple Watch Series 6, 7, and 8.
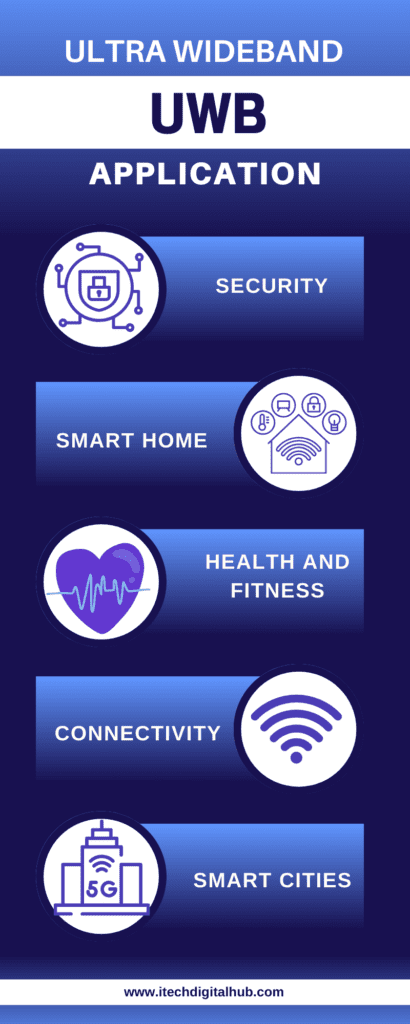
- Gesture recognition: By detecting changes in the distance between the transmitter and receiver, UWB may be used to track the location of people or things. Self-driving cars, smart appliances for homes, and controllers for gaming all make use of such technology.
- Asset tracking: Ultra wideband helps find things like shipping containers or livestock. Businesses benefit from it by being more efficient and secure.
- Crowd management: UWB technology can be used to track the movement of people in crowded areas such as stadiums or live music concerts to increase security and safety.
- Navigation: UWB is great for indoor navigation, finding a bike nearby, driverless valet parking, and pick-up.
- Sport: Ultra-wideband (UWB) is a technology used in the NFL to keep track of where players are on the field. UWB antennas are placed inside footballs, which update the ball’s location 2,000 times every second. This technology will allow for more advanced statistics, officiating, and animations in the future when watching sports.
What are the benefits of UWB?
The advantages of UWB are as follows:
High data rates: Compared to Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, UWB may reach data speeds of up to 100 Mbps.
Accurate device location tracking: UWB can determine a gadget’s position to within centimeters.
Low power consumption: UWB is perfect for battery-powered gadgets since it uses very little electricity.
Security: UWB is a safe wireless technology that is capable of withstanding interference and listening devices.
Good noise immunity: UWB signals are less susceptible to interference from other wireless signals, making them more reliable in noisy environments.
Penetration of materials: UWB signals can penetrate walls and other obstacles, making it ideal for indoor positioning and tracking applications.
What are the challenges of UWB?
The disadvantages of UWB are as follows:
Limited range: UWB is only capable of serving in short-range areas.
Interference: Other wireless transmissions may cause UWB to experience interference.
Cost: Compared to other wireless devices like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, UWB devices are currently more costly.
Regulatory issues: UWB operates in a frequency band that is regulated by governments, which can limit its use in certain regions.
FAQs
- How accurate is UWB technology?
UWB technology uses short pulses and precise measurements, allowing it to achieve precise location accuracy down to centimeters. - Is UWB safe?
Yes, UWB is safe, just like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. It’s a radio-based communication standard. - What is the History of UWB?
UWB has been around since the early days of radio. It was first used by the US military and later in consumer products in the late 2010s. - Can UWB go through walls?
Yes, UWB signals can go through some walls, depending on their thickness and material. - Does UWB need a direct line of sight?
No, UWB works even with barriers between devices. It doesn’t require a direct line of sight, although accuracy decreases compared to Bluetooth.
Conclusion
Ultra Wideband (UWB) technology is fast, uses less power, and can pinpoint locations really accurately. It is best suited for various sectors, including gaming, smart gadgets, self-driven cars, augmented reality, sports, and other industries. With UWB, we can track things in real time, create wireless sensor networks, manage assets, and have secure communication.
